Emeramide: Features of a unique chelator
Emeramide is an exceptionally safe antidote for heavy metal poisoning and also a powerful antioxidant. There are plans underway to get it approved by the USFDA.
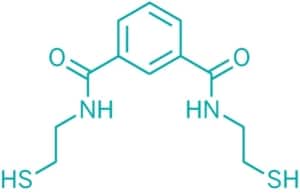 Emeramide was first introduced to the dental/medical community in 2008 as an antioxidant supplement with adverse reporting tracked. It is made from two natural substances we eat every day. The first building block is carboxyl benzoate which is found naturally in cranberries. Carboxyl benzoate is widely used as a preservative in many foods and drinks and generally recognized as a safe compound. Two arms are made out of cysteamine (found naturally in meat and on the terminal end of Co-enzyme A) which is also a widely used natural antioxidant. The cysteamines have a sulfhydryl (-SH) at their terminal ends, and the amino ends are attached on the 1st and 3rd carbon groups of the carboxyl benzoate. This allows the -SH groups to flex, rotate and take many different positions to accommodate the binding parameters of several toxic metals that are attracted to -SH groups, which covers most toxic heavy metals.
Emeramide was first introduced to the dental/medical community in 2008 as an antioxidant supplement with adverse reporting tracked. It is made from two natural substances we eat every day. The first building block is carboxyl benzoate which is found naturally in cranberries. Carboxyl benzoate is widely used as a preservative in many foods and drinks and generally recognized as a safe compound. Two arms are made out of cysteamine (found naturally in meat and on the terminal end of Co-enzyme A) which is also a widely used natural antioxidant. The cysteamines have a sulfhydryl (-SH) at their terminal ends, and the amino ends are attached on the 1st and 3rd carbon groups of the carboxyl benzoate. This allows the -SH groups to flex, rotate and take many different positions to accommodate the binding parameters of several toxic metals that are attracted to -SH groups, which covers most toxic heavy metals.
The amino acid hands terminate with a sulfur group on the free end that heavy metals strongly bind to. There are movable bonds at the carbon and the nitrogen atoms that allow the arms to freely move in any direction to grasp various metal atoms such as mercury.
Emeramide: A History of Success
About 2.5 million doses of the original Emeramide compound were sold as the supplement OSR#1® (Oxidative Stress Relief) with no significant adverse reactions reported to the listed adverse effects reporting site on the OSR containers nor to the FDA. There were, however, numerous anecdotal reports of remarkable recoveries that have guided the research required for drug development. Initial studies supported the safety of OSR#1® as a food supplement. Three clinical trials required for drug development have further established safety. The Phase 1 safety study and Phase 2 clinical trials showed no adverse effects in humans. Available in the USA through the FDA as an investigative new drug (IND) which also requires monitoring by an institutional review board (IRB), or right-to-try.
Why is Emeramide so Effective?
Emeramide is soluble in lipophilic, fatty tissues. Once it encounters a heavy metal, such as mercury, Emeramide fully combines with that metal to quickly render the metal chemically inert and nontoxic. The Emeramide mercury complex (Em/Hg) is insoluble in fat, water, acid or base. Furthermore, it takes 230 degrees Celsius to break apart the firm bond between Emeramide and mercury. Experiments have shown that the Em/Hg complex is removed from the body by the P-450 detox system which attaches a charged water soluble group to the complex, marking it for excretion through the bowel as is commonly done for many water insoluble compounds and drugs.
Emeramide has been shown to be extremely safe
Safety studies in at least four species of animals have also found no evidence of toxicity at levels used in treating humans for metal toxicities. Studies in humans for 30 days at 300 mg per day and 10 days at 600 found no adverse events and no depletion of any of the normal essential minerals. Animals given large quantities of the preformed Em/Hg complex found no evidence of harm.
How to obtain Emeramide
Emeramide is now available in many countries throughout the world. In the USA it is available as an Investigative New Drug (IND) with an Institutional Review Board (IRB) to supervise the informed consents and results of treatment.